BECE 2009 Integrated Science Objective Questions and Answers
Answer all questions in this section.
Each question is followed by four options lettered A to D. Find the correct answer for each question.
1. Plants are different from animals because they
Solution: Chlorophyll is unique to plants and is essential for photosynthesis, a process animals cannot perform. While both plants and animals respire, reproduce, and have protoplasm, chlorophyll distinguishes plants.
2. Which of the following conditions is **not** required for a current to flow through an electric circuit?
Solution: A bulb is not necessary for current flow; it is merely an example of a load. Current requires a closed circuit, a power source (e.g., battery), and conductors (wires).
3. Which of the following examples is a source of energy?
Solution: Wood is a primary energy source (biomass) that can be burned to release energy. Electricity, heat, and light are forms of energy, not sources.
4. Heat is transferred from the bottom of water in a container to the top by
Solution: Convection involves the movement of heated fluid (water) upward, displacing cooler fluid downward, creating a circular flow.
5. A mercury thermometer works on the principle that
Solution: Mercury (a liquid) expands when heated and contracts when cooled, causing the level in the thermometer to rise or fall.
6. In which of the positions Q, R, S, T in the diagram below will a body have the greatest potential energy?
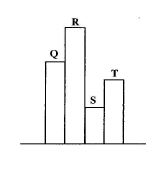
Solution: Potential energy is highest at the highest point (R) due to its elevation relative to the ground.
7. A solar cell produces electrical energy from
Solution: Solar cells convert sunlight (light energy) directly into electrical energy via the photovoltaic effect.
8. In a third class lever the
Solution: In a third-class lever, the effort is applied between the pivot (fulcrum) and the load (e.g., tweezers or a human arm).
9. At which positions S, R, Q and P on the lever in the diagram below must a force be applied to lift the load most easily?
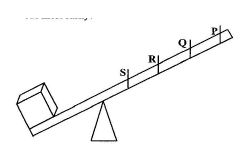
Solution: Applying force farthest from the pivot (P) maximizes torque, making it easier to lift the load.
10. Which of the following machines works on the same principle as an inclined plane?
Solution: A screw is an inclined plane wrapped around a cylinder, reducing the force needed to lift or hold objects.
11. Power is defined as the
Solution: Power measures how quickly work is done (work/time), e.g., watts (Joules/second).
12. Which of the following food substances is not involved in respiration?
Solution: Respiration breaks down glucose, fatty acids, and amino acids for energy, but vitamins are micronutrients, not energy sources.
13. Which of the following organisms is at the beginning of a food chain?
Solution: Grass is a producer (autotroph), forming the base of food chains by converting sunlight into energy.
14. The human male sex cell that takes part in reproduction is the
Solution: Sperm is the male gamete that fertilizes the female egg; other options are organs or structures.
15. The removal of waste products from the cells of organisms is called
Solution: Excretion eliminates metabolic wastes (e.g., urea, CO₂) from cells.
16. The central nervous system consists of the
Solution: The CNS comprises the brain and spinal cord; nerves are part of the peripheral nervous system.
17. Which of the following life processes is **not** performed by all living things?
Solution: Photosynthesis is unique to plants/algae; animals respire, excrete, and reproduce but do not photosynthesize.
18. All veins in the body carry blood that does not contain oxygen with the exception of the veins from the
Solution: Pulmonary veins carry oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart; other veins carry deoxygenated blood.
19. The method of purification of water containing very little impurities is
Solution: Distillation removes even dissolved impurities by boiling and condensing water, yielding pure H₂O.
20. Boiling and chlorination are used in water purification to
Solution: Boiling kills pathogens, and chlorination disinfects; neither removes particles or hardness.
21. The chemical symbol **C** is the symbol for
Solution: The symbol **C** represents carbon in the periodic table; calcium is Ca, chlorine is Cl, and sodium is Na.
22. A substance which is made up of the same kind of atoms is called
Solution: Elements consist of identical atoms (e.g., pure gold), while compounds/mixtures contain multiple elements.
23. Which of the following processes results in the formation of new substances?
Solution: Saliva contains enzymes that chemically break down starch in yam, forming new substances (chemical change).
24. When elements combine to form a compound the
Solution: Compounds have fixed ratios represented by formulas (e.g., H₂O), unlike mixtures which can vary.
25. Which of the following organisms is likely to increase the oxygen content of the water in a pond?
Solution: Water lilies are plants that release oxygen during photosynthesis, unlike animals which consume oxygen.
26. Which of the following parasites is a plant?
Solution: Dodder is a parasitic plant; others are animal parasites (Bilharzia=flatworm, lice=insect, tapeworm=worm).
27. The part of the soil that is most important for the growth of plants is
Solution: Humus provides nutrients and improves soil structure, unlike inert mineral particles (clay/sand/silt).
28. Which of the following diseases may be associated with water?
Solution: Cholera spreads through contaminated water; others are viral (chicken/small pox) or soil-borne (tetanus).
29. The mosquito and housefly are harmful in that they
Solution: Both are disease vectors (mosquitoes=malaria, houseflies=typhoid), though blood-sucking applies only to mosquitoes.
30. Which of the following diseases affects the central nervous system?
Solution: CSM inflames brain/spinal cord membranes; polio affects motor neurons (PNS), while measles/yellow fever are systemic.
31. Day and night occur because the earth
Solution: Earth's 24-hour rotation causes alternating daylight/darkness; orbital motion (A) causes seasons.
32. Bronze is an alloy of
Solution: Bronze is Cu+Sn; brass is Cu+Zn, steel is Fe+C.
33. Which of the following substances causes acid rain when released into the atmosphere?
Solution: SO₂ forms sulfuric acid in rain; CO₂ causes weak carbonic acid but not "acid rain."
34. Which of the following gases helps in rusting?
Solution: Rusting (iron oxidation) requires O₂ + water; other gases don't participate.
35. The force of attraction between molecules of different substances is called
Solution: Adhesion=between unlike molecules (e.g., water on glass); cohesion=between like molecules (water-water).
36. A metal block has a mass of 0.1kg. Calculate its volume if the density is 1.0 kgm⁻³.
Solution: Volume = mass/density = 0.1kg ÷ 1kg/m³ = 0.1 m³.
37. The food manufactured by a plant is distributed to all parts of the plant through the
Solution: Phloem transports sugars (food); xylem moves water, stomata are pores, chlorophyll is a pigment.
38. Some insects are able to walk on water because
Solution: Surface tension creates a "skin-like" surface that supports lightweight insects.
39. Oxygen is made available to all cells of the human body by the
Solution: RBCs contain hemoglobin that binds O₂; other components don't transport oxygen.
40. The force which pulls all objects towards the centre of the earth is the
Solution: Gravity is the attractive force between masses; Earth's gravity pulls objects toward its center.
1. Question 1
1. (a) In an experiment, four nails 1, 2, 3 and 4 are fixed with candle wax onto a metal bar and one end of the bar is heated by means of boiling water as shown in the diagram below.
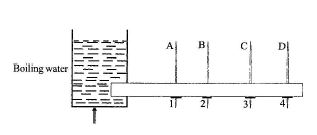
(i) What is the temperature of the boiling water?
(ii) State the observations that will be made about nails 1, 2, 3 and 4.
(iii) State the observations that will be made about the temperatures recorded by thermometers A, B, C and D.
(iv) What mode of heat transfer is demonstrated in the experiment?
(v) State one effect of heat that is associated with the experiment.
(vi) State the aim of the experiment.
(b) In an experiment, a student took three iron nails and cleaned their surfaces dry and placed them in three separate test tubes in set-ups A, B and C as shown in the diagram.
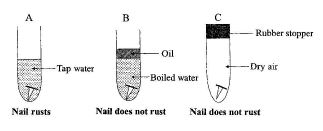
(i) Why was the water in set-up B boiled?
(ii) Explain the function of the oil on top of the water in set-up B.
(iii) State the purpose of the rubber stopper in set-up C.
(iv) Why did the nail in set-up A rust?
(v) Suggest an aim for the experiment.
(vi) From the experiment, explain why oil or grease is applied on the surface of a metal to prevent rusting.
(c) In an experiment the following activities were carried out on two green leaves A and B. Leaf A was from a plant placed in the sunlight for sometime while leaf B was from a plant placed in a dark cupboard for 24 hours.
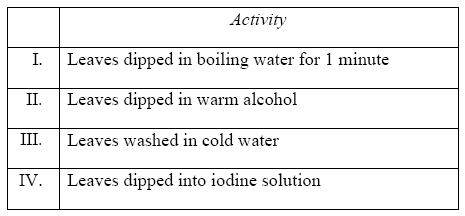
(i) Explain why each of the activities I, II, III and IV was carried out.
(ii) State the colour change of leaf A.
(iii) Explain why leaf A changed colour but leaf B did not.
(iv) Suggest an aim for the experiment.
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 1
1. (a) (i) Temperature = 100°C or 212°F or 373K.
(ii) Observations (Nails): Nails 1, 2, 3 and 4 will drop off one after the other – Nail 1 drops first, nail 2 second, nail 3 third and nail 4 fourth.
(iii) Observations (Thermometers): The readings of Thermometers A, B, C and D will increase progressively till they reach 100°C – Thermometer A reaches 100°C first, B second, C third and D fourth.
(iv) Mode of heat transfer: Conduction.
(v) Effects of heat:
- Causes increase in temperature (as shown by the thermometer readings).
- Causes change in state (candle wax melts – changes from solid to liquid).
(vi) Aim of experiment:
- To show that metals are good conductors of heat.
- To show that heat travels through metals.
(b) (i) To remove dissolved air / oxygen from the water.
(ii) To prevent air (hence, oxygen) from entering / getting dissolved in the water.
(iii) To prevent water particles or vapour or moisture from entering and contacting the nail.
(iv) Because it was exposed to both water and oxygen (air), which are necessary for rusting.
(v) To show that moisture/water and oxygen/air are necessary for rusting to occur.
(vi) To prevent moisture and air, which contains oxygen, from getting into contact with the metal, since metals containing iron will rust in the presence of air and moisture.
(c) (i) - I: To kill the plant cells or stop the process of photosynthesis.
- II: To remove the green pigment (chlorophyll).
- III: To wash away the alcohol and soften the leaf.
- IV: To test for starch in the leaf.
(ii) From cream / pale yellow / light brown to blue-black.
(iii) The blue-black colouration indicates the presence of starch, which means that photosynthesis occurred in leaf A to produce starch. Leaf B did not change in colour because photosynthesis did not occur, and hence, no starch was produced.
(iv) To demonstrate that light is necessary for photosynthesis to occur and produce starch.
2. Question 2
2. (a) Explain each of the following observations in nature:
(i) In the depths of the ocean where it is always dark, there are no green plants.
(ii) On an island where there are no insects and birds, the pawpaw plant produces only flowers but no fruits.
(b) Describe how soil is formed.
(c) (i) State the laws of reflection.
(ii) Draw a labelled diagram to show the reflection of light on a plane mirror.
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 2
2. (a) (i) No light reaches there, hence no photosynthesis takes place.
(ii) Since there are no agents of pollination, no pollination takes place; hence, no fertilization takes place. As a result, no fruits are produced.
(b) Soil is formed from the disintegration/breakdown/weathering of rocks. The broken down rock particles combine with water, decayed organic matter, air and micro-organisms to form soil.
(c) (i) - The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
- The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal, at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane.
(ii) 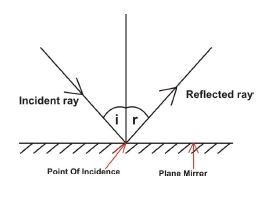
(i = angle of incidence, r = angle of reflection)
3. Question 3
3. (a) A child is found not to be able to see at night.
(i) What deficiency disease may the child be suffering from?
(ii) What food nutrient is the child lacking?
(iii) List two sources of food substances that can provide the nutrient the child lacks.
(b) (i) What is an atom?
(ii) Name the components of an atom which determines each of the following quantities.
(α) mass of an atom
(β) charge of an atom
(iii) Why is an atom electrically neutral?
(c) (i) What is friction?
(ii) Give two bad effects of friction.
(iii) Give two situations where friction is an advantage.
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 3
3. (a) (i) Deficiency disease: Night blindness.
(ii) Food nutrient: Vitamin A.
(iii) Food sources: Milk, butter, cheese, egg yolk, liver, palm oil, tomatoes, carrots, lettuce, cod-liver oil.
(b) (i) - The smallest particle of a substance that can take part in a chemical reaction.
- The smallest portion into which an element can be divided and still retain its properties.
(ii) (α) mass of atom: protons and neutrons.
(β) charge of atom: protons and electrons.
(iii) The numbers of protons and electrons are equal. The positively charged protons neutralize the negatively charged electrons, hence, making the atom electrically neutral.
(c) (i) - The force that opposes the relative sliding motion of two bodies in contact.
- The resistance encountered by an object moving relative to another object with which it is in contact.
(ii) - Reduces the efficiency of machines.
- Causes wear and tear.
- Causes loss of energy through heat generation.
- Slows down sliding motion of a body.
(iii) - Enables walking, running, etc without slipping.
- Enables vehicles to brake effectively.
- Enables birds to perch on trees without falling.
- Enable wheels to roll on a surface.
- Enables our hands to hold items.
4. QUESTION 4
4. (a) (i) Explain heredity.
(ii) Give two examples of heredity characters.
(b) Explain whether each of the following processes is a chemical change or a physical change:
(i) Rusting;
(ii) Burning;
(iii) Filtration;
(iv) Expansion of copper.
(c) (i) What is a simple machine?
(ii) Name two types of simple machines.
(iii) Explain why the efficiency of a machine cannot be equal to 100%.
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 4
4. (a) (i) The passing on of genetic factors from parents to children through genes. Or: the transfer of genetically controlled characteristics from one generation to the next in living organisms.
(ii) Examples: Intelligence, shape of nose, height, colour of eyes, etc.
(b) (i) Rusting - Chemical change; because a new substance is formed and the change is irreversible.
(ii) Burning - Chemical change; because a new substance is formed and the change is irreversible.
(iii) Filtration - Physical change; because no new substance is formed and the change is reversible.
(iv) Expansion of copper - Physical change; because no new substance is formed and the change is reversible.
(c) (i) A mechanical device that makes work easier and/or faster.
(ii) Inclined plane, wheel and axle, lever and pulley.
(iii) Part of the energy input is used to overcome friction and part also expended as heat.
5. QUESTION 5
5. (a) Study the organisms listed below:
Earthworm; Sheep; Cassava plant; Grasshopper; Man; Hen.
Draw a food chain using four of the organisms.
(b) (i) Name four types of forces apart from friction.
(ii) Give three effects of a force.
(c) A certain pupil in a classroom can see clearly on the blackboard only when he sits at the front.
(i) State the eye defect the child is suffering from.
(ii) Explain why the child is unable to see when he is far from the blackboard.
(iii) How can the defect be corrected?
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 5
5. (a) - Cassava plant → grasshopper → hen → man.
- Cassava plant → earthworm → hen → man.
(b) (i) Gravitational, tensional, centripetal, centrifugal, magnetic, electrostatic, upthrust, cohesive, adhesive.
(ii) - Can cause a moving body to come to rest (stop moving).
- Can cause a body at rest to move.
- Can cause a moving body to accelerate.
- Can cause a moving body to decelerate.
- Can change the direction of a moving body.
- Can change the shape of a body.
(c) (i) The eye defect: shortsightedness or myopia.
(ii) Light rays from a distant object are focused in front of the retina, due to the eye lens being thicker than normal or eyeball being too long. Hence the brain does not receive the correct information for interpretation and so the child is unable to see.
(iii) By the use of a concave or diverging lens.